Primero la vida
Primero la vida
 Results
Results
Results
May 29, 2025
Waste generation and Management
Integrated waste management is a key component of the actions implemented under the framework of operational excellence, supporting the environmental strategy and the Circular Economy model of the Ecopetrol Group. All initiatives are carried out in compliance with national regulations and Ecopetrol S.A.’s internal procedures.
Ecopetrol has developed a material and waste roadmap to guide its transition toward a Circular Economy, recognizing it as a strategic enabler to close material and waste loops. This roadmap includes specific targets for waste reduction and reuse, enabling the measurement and enhancement of circularity performance.
From an operational excellence perspective, the company is implementing comprehensive waste management actions focused on the adoption, reuse, and treatment of generated waste, with the goal of minimizing final disposal in sanitary landfills. These efforts are aligned with our long-term objective:
“Progressive reduction of waste sent to final disposal by 2040”and support our broader business ambition within the circularity framework.
Source: Data was obtained from SAP-Waste Management (SAP-WA) for the periods 2021 – 2022. For 2023, and 2024 the data is extracted from MARS-E tool
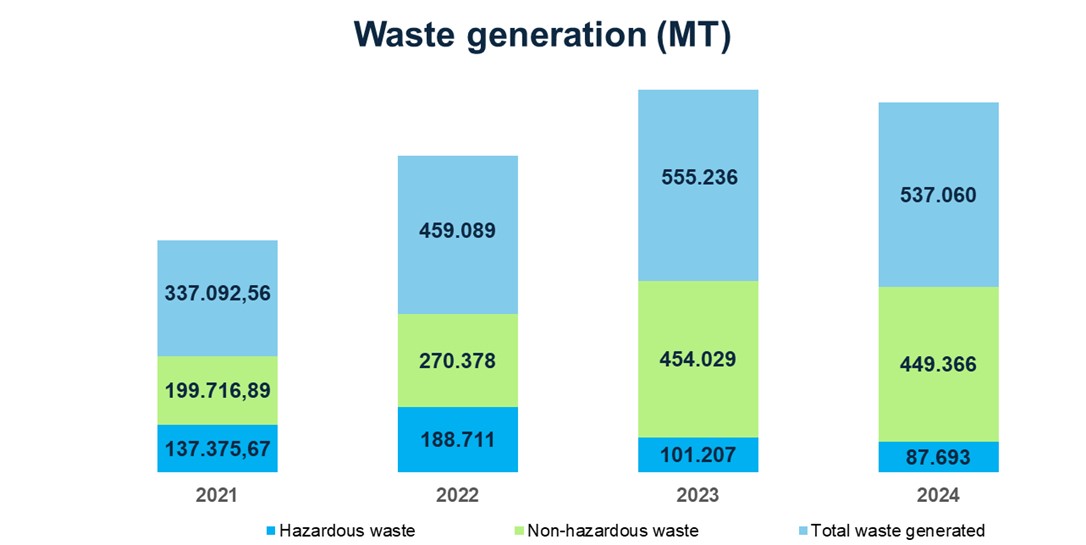
In 2024, a total of 537,060 MT of waste where generated, of which 87,693 MT were hazardous waste and 449,366 MT were non-hazardous waste. This represents a 3% reduction in total waste generation compared to 2023. Non-hazardous waste generation decreased by 1% compared to 2023, primarily due to a reduction in the generation of scrap metal.
On the other hand, hazardous waste generation in 2024 shows a 13% decrease compared to 2023, mainly due to a reduction of oil sludge associated with: Oily sludge (i) lower number of periodic maintenance carried out during 2024, (ii) implementation of oil recovery treatments present in sludges, which is subsequently reintegrated into the operations at Casabe asset, and (iii) Implementation of initiatives enabling the dehydration of oily sludge at the Rubiales asset, Regarding oil-based cuttings, there was a 33% reduction compared to 2023, mainly due to a decrease in drilling campaigns in the Piedemonte asset and finally, for hydrocarbon-contaminated soils, a 16% reduction was recorded compared to 2023, primarily due to a decrease in the number of barrels spilled during environmentally impactful incidents.
Hazardous waste generated, in descending order of quantity, includes: oil sludge 60.496 MT, hydrocarbon-contaminated soils 12.373 MT, and oil-based drilling cuttings 6.145 MT.
Regarding the total non-hazardous waste generated, the most representative categories are: construction and demolition waste (CDW) 285.390 MT, water-based drilling cuttings 107.697 MT, and metal scrap 27.102 MT.
The Information about waste management is available in the MARS-E tool which allows the monitoring of the quantities generated for each waste stream.
Note: The 2023 hazardous waste figure was adjusted based on the official information released after the report was submitted, from 114,990 MT to 101,207 MT.
Waste Normalization
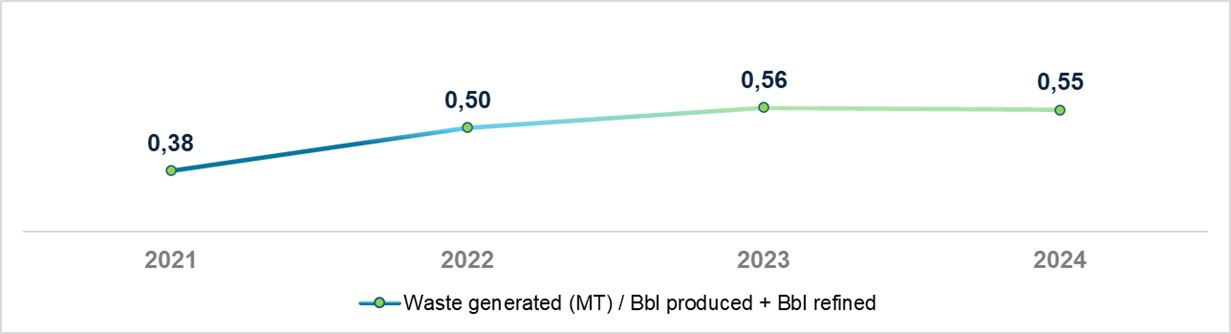
Over the past four years, total waste generation has been increasing. However, a 2% reduction was achieved in 2024. While the waste intensity—measured as waste generated per barrel of oil produced and refined—increased through 2023, a downward trend was achieved for 2024.
It is important to note that waste generation is not limited to production and refining operations. Other activities such as facility maintenance, construction, and demolition also contribute significantly to overall waste volumes.
The improvement in this indicator reflects enhanced operational efficiency in waste management practices and underscores our ongoing commitment to sustainability.
Source: Data was obtained from SAP-Waste Management (SAP-WA) for the periods 2021 – 2022. For 2023 and 2024, the data is extracted from MARS-E tool.
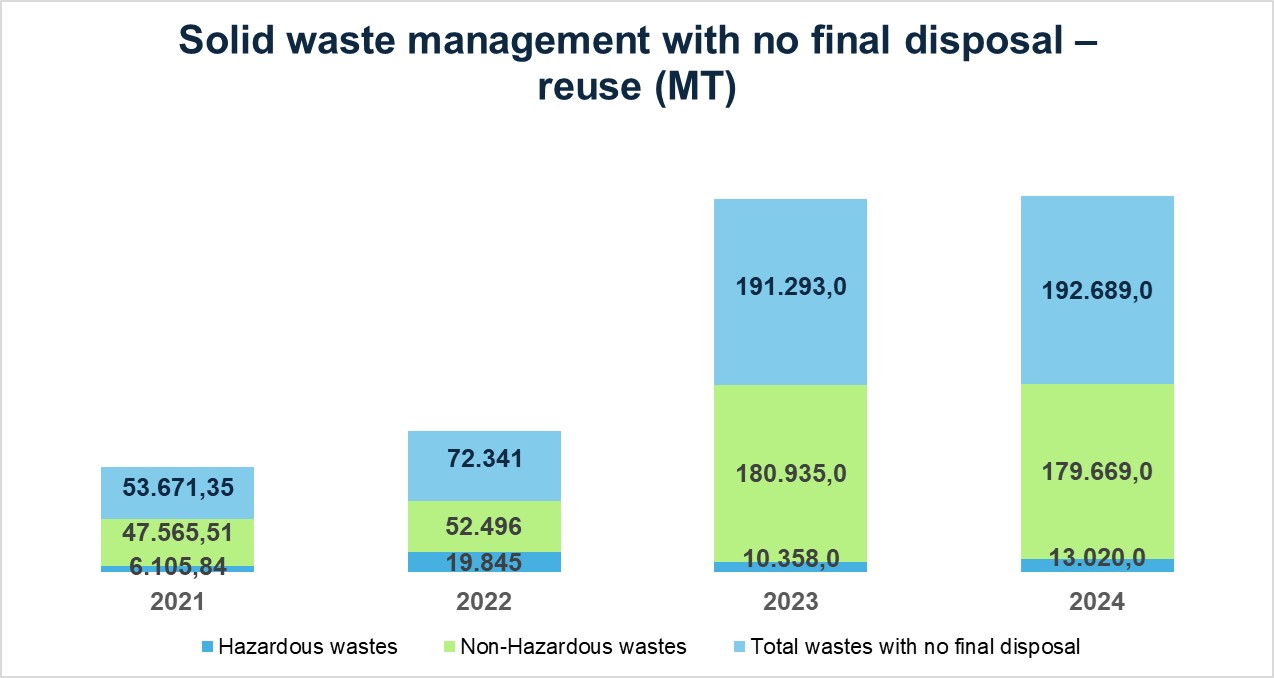
Ecopetrol achieved a 36% waste recovery rate in 2024, a 2% increase compared to 2023.
The Company recovered 15% of the hazardous waste generated (+5% compared to 2023) by utilizing oily sludge and hydrocarbon contaminated soils in cement kilns within the Downstream sector. Additionally, 47 MT of used lubricating oils were recovered, primarily in the fluid treatment system at the Cartagena refinery.
The Company also recovered 40% of its non-hazardous waste, driven by the following initiatives:
- Utilized 142,291 MT (50%) of construction and demolition waste (CDW) for maintaining internal and external roads and building civil works.
- Transferred 27,101 MT of scrap metal to the steel industry for recovery, achieving a 99% recovery rate.
- Recovered 1,682 MT (94%) of organic waste through composting and silage, generating fertilizers and other byproducts for internal use and delivery to Stakeholders
In terms of plastics, glass, paper, and cardboard, Ecopetrol achieved a 98% recovery rate by donating these materials to individuals or foundations engaged in recycling.
It is worth noting that 93% to 98% of waste such as plastic, glass, paper, and cardboard is recycled through distribution to individuals or foundations that manage this waste.
Information on waste utilization is obtained through reports from the contractor companies that carry out the activities.
All waste recovery data is based on reports submitted by the contractor companies responsible for executing the waste management activities.
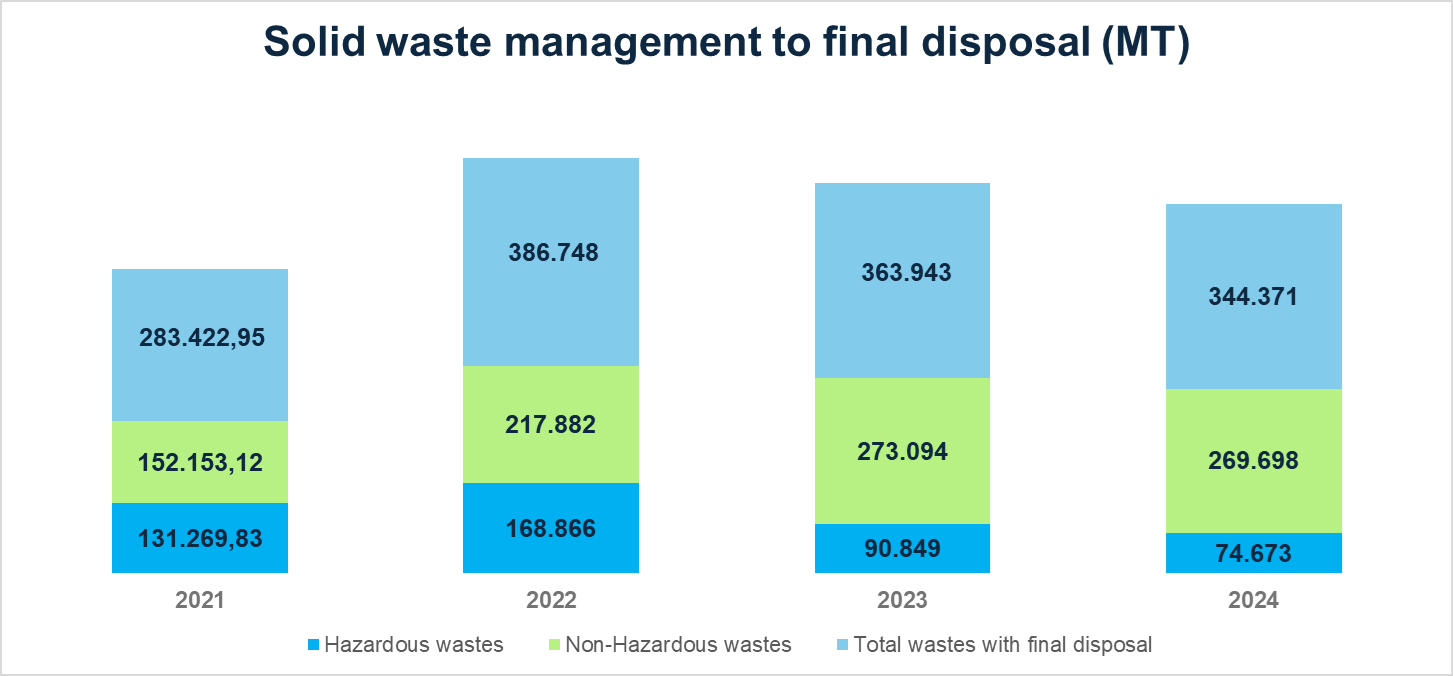
Source: Data was obtained from SAP-Waste Management (SAP-WA) for the periods 2021 – 2022. For 2023 and 2024, the data is extracted from MARS-E tool.
According to the Integral waste management guide, part of the management stages is the waste verification which involves the determination if the waste is susceptible to reduction and/or utilization. If the waste's physicochemical composition is not adequate or there is no available reuse or treatments alternatives in the market for these compounds, all the waste is sent to final disposal processes.
In 2024 the main waste sent for final disposal or elimination were:
- Construction and demolition waste (CDW)
- Water-based drilling cuttings
- Oily sludges
- Hydrocarbon-contaminated soils
Construction and demolition waste (CDW), as well as water-based drilling cuttings, are mainly disposed of in areas where excavation material is disposed of or internal/external authorized landfills.
The data also includes waste such as oily sludges and hydrocarbon-contaminated soils, which constitute about 83% of the company's hazardous waste in 2024, 45% were treated through bioremediation, this treatment is carried out in the installations of authorized third parties.
Hazardous waste destined for disposal were placed in cells or sanitary landfills, e.g. sludges with acidic characteristics and elements impregnated with hydrocarbons.
The collection of information for waste designated for disposal, such as oily sludges, hydrocarbon-contaminated soils, elements impregnated with hydrocarbons, and catalysts, among others, is carried out through reports from contractor companies that carry out activities within industrial facilities.
In 2024, solid waste generation decreased by 18,176 metric tons, primarily due to a reduction in metal scrap volumes, fewer maintenance activities, fewer drilling campaigns, and a lower number of environmental incidents involving hydrocarbon spills.
Notably, there was a 2% reduction in total waste sent to final disposal, representing 19,572 metric tons less than in 2023. This progress reinforces our commitment to the gradual minimization of waste destined for final disposal, in alignment with our sustainability objectives.
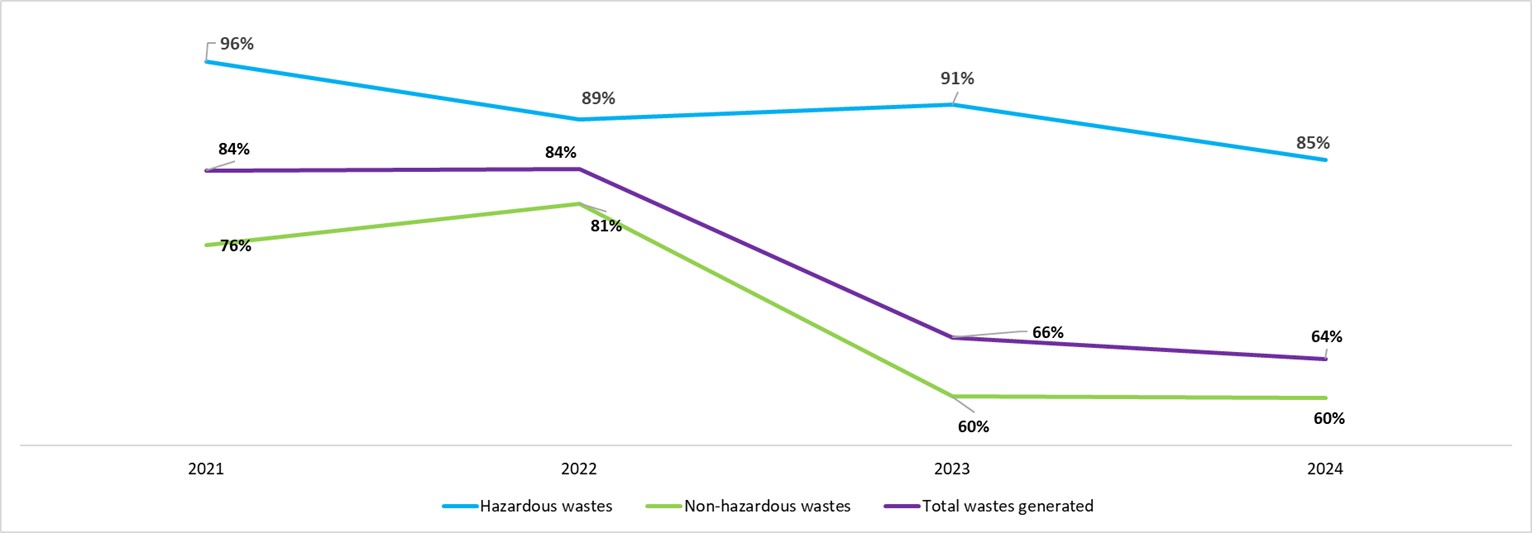
In 2024, Ecopetrol sent 85% of hazardous waste and 60% of non-hazardous waste to final disposal, resulting in an overall disposal rate of 64% of total waste generated. This represents a 2% reduction compared to 2023, reflecting continued progress toward minimizing waste sent to final disposal.
All waste management activities are carried out in full compliance with applicable regulations and legislation, and in alignment with the highest industry standards and best practices. Compliance is verified through a monitoring program that oversees waste management conditions across both internal and external facilities.
Research and Development
In 2024, the Colombian Institute of Petroleum and Energy Transition (ICPET) invested over 4,000 million Colombian pesos (MCOP) in research projects focused on the recovery and valorization of waste streams, including construction and demolition waste (CDW), used lubricating oil, spent sulfuric acid, pyrolysis oil, and single-use plastics through chemical recycling technologies. Additionally, research was conducted on the use of oily waste as asphalt binder.
These initiatives contribute significantly to reducing the volume of waste sent to final disposal, supporting Ecopetrol’s commitment to circular economy principles and sustainable waste management.
Skills improvement
During 2024, 101 employees received training in Integrated Waste Management (IWM) through Ecopetrol University with a total of 2 hours dedicated to this training. The historical report of this formation in recent years is:

|
Integrated Waste Management (IWM) |
||||
|
Year |
2021 |
2022 |
2023 |
2024 |
|
Trained employees |
396 |
128 |
862 |
101 |