|

|
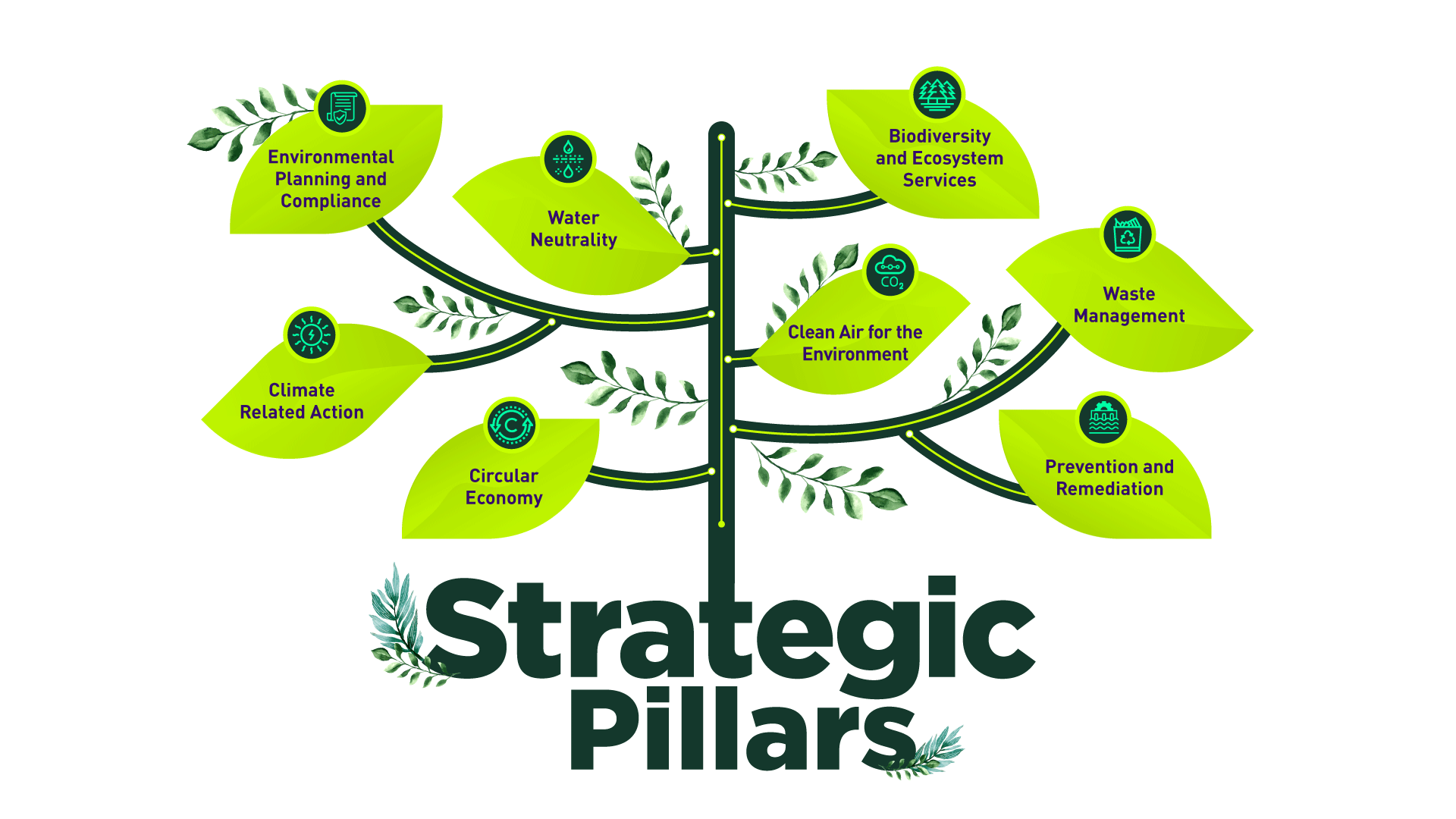
Environmental Planning and Compliance
The prior knowledge and diagnosis of environmental aspects and determinants, as well as the specific regulations of the areas where Ecopetrol S.A. carries out projects and operations allow the identification of potential environmental impacts and essential opportunities for the conception and planning of measures focused mainly on the application of the mitigation hierarchy, contributing to the successful development of operations, the viability of new projects and the sustainable development of the territories where it operates.
|
|

|
Climate related action
Ecopetrol remains committed to reducing its carbon footprint and thus joining efforts to limit the increase in global temperature to below 1.5 ° C. To do this, it carries out actions to reduce carbon emissions both in operations and in the Company's value chain, reduce the vulnerability of the operation to variability and climate change, as well as adequately manage risks and identify opportunities in relation to climate change
|
|

|
Water Neutrality
The goals associated with water management in the world are framed in the Sustainable Development Goal 6, which seeks to guarantee universal access to drinking, safe and affordable water for all by 2030. Therefore, the comprehensive water management in Ecopetrol must contribute to the equitable, economic and environmental sustainable provision of water resources, articulated with Ecopetrol's Corporate Strategy, the TESG agenda, the water neutrality roadmap, and the strategic pillars of action for climate, biodiversity and circular economy
|
|

|
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
The biodiversity strategic line seeks to generate a positive net impact on biodiversity and ecosystem services, meeting the expectations of the main stakeholders and maintaining the license to operate, through proper management. It has four main axes: i) Mitigation hierarchy, ii) Nature-based solutions iii) Knowledge generation, and iv) Biodiversity culture.
|
|

|
Circular Economy
The Environment and Sustainable Development Ministry and the Commercial Ministry have defined Circular Economy, in the Circular Economy National Strategy, as a "Production and consumption system that promotes the efficient use of materials, water and energy, considering the recovery capacity of ecosystems, the circular use of material flows through the implementation of technological innovation, alliances and collaboration among actors, and the promotion of business models according to the foundations of sustainable development”.
In this sense, the circular economy is adopted as a driver that contributes to the energy transition, the goal of zero net carbon emissions, water footprint reduction, closed-loop cycle of material and waste, and the diversification of new businesses, to ensure the competitiveness and long-term sustainability of the Company, while striving for the conservation of natural resources and society’s well-being.
|
|

|
Clean Air for the Environment
Estimate the contribution in the reduction of atmospheric emission criteria contaminants, and/or in the improvement of air quality based on decarbonization projects, energy transition, clean fuels, strategic environmental investment, and mandatory environmental investment (1% and offsets).
|
|

|
Waste Management
This strategic pillar includes the implementation of operational and organizational measures intended to reduce (to economic and technically feasible levels) the quantity and danger of the waste generated, based on three (3) fundamental aspects: a) Reduction at the source or origin; b) Recovery of material through the use of waste, via the implementation of the Multi-R or 9Rs concept of circular economy; c) Incorporation of disruptive technologies
|
|

|
Prevention and Remediation
This pillar focuses on the prevention of operational incidents that affect the environment, incorporating proactive risk management and the analysis of potential materialization of environmental risks inherent in the various business areas
|
 Web Content Viewer
Web Content Viewer
 buscador
buscador
 Web Content Viewer
Web Content Viewer