 PautaInternas
PautaInternas
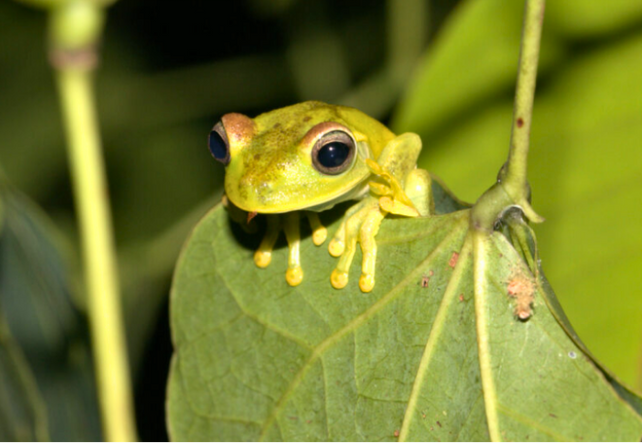
 Environmental compensation and forced investment of 1%
Environmental compensation and forced investment of 1%
Compliance to biodiversity offsets and 1% investment requirements
May 2, 2025
Compliance strategy

Within the mitigation hierarchy framework, Ecopetrol complies with regulatory biodiversity offsets to achieve biodiversity no net lossno and adheres to the *mandatory investment of no less than 1%, enacted when freshwater withdrawals from natural sources occur, aimed at protecting, restoring, or surveilling the river basin. Such investments materialize through conservation strategies that include preservation, restoration of strategic ecosystems and sustainable use of biodiversity, in collaboration with local communities, state institutions such as IDEAM, and implementing partners in the territory.
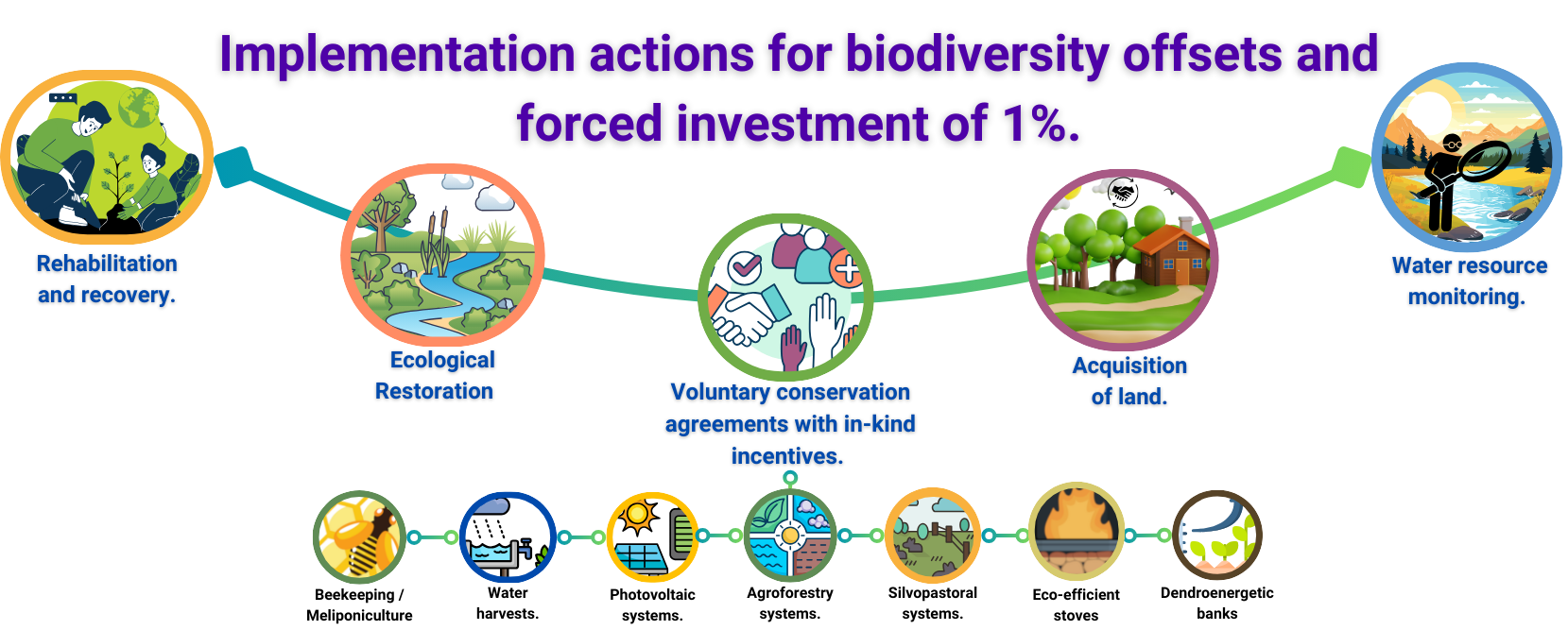
Activities include i) signing of conservation agreements with in-kind payments to promote the preservation/rehabilitation strategic ecosystems (e.g riparian forests, morichales), ii) acquiring private lands that encompass relevant areas for biodiversity conservation and delivering them to government institutions for their preservation, iii) protective reforestation with native species, iv) restoration approaches outlined in the national restoration plan (reclamation, rehabilitation and ecological restoration) and v) enhancing river basin surveillance through acquiring monitoring equipment and technology (solely within 1% investment). It should be noted that each of these actions are previously approved by the environmental authority and are developed in prioritized areas that consider national and regional planning instruments, areas of influence of the operation and projects, biodiversity information on a national scale, among others.
Biodiveristy cores of Ecopetrol S.A 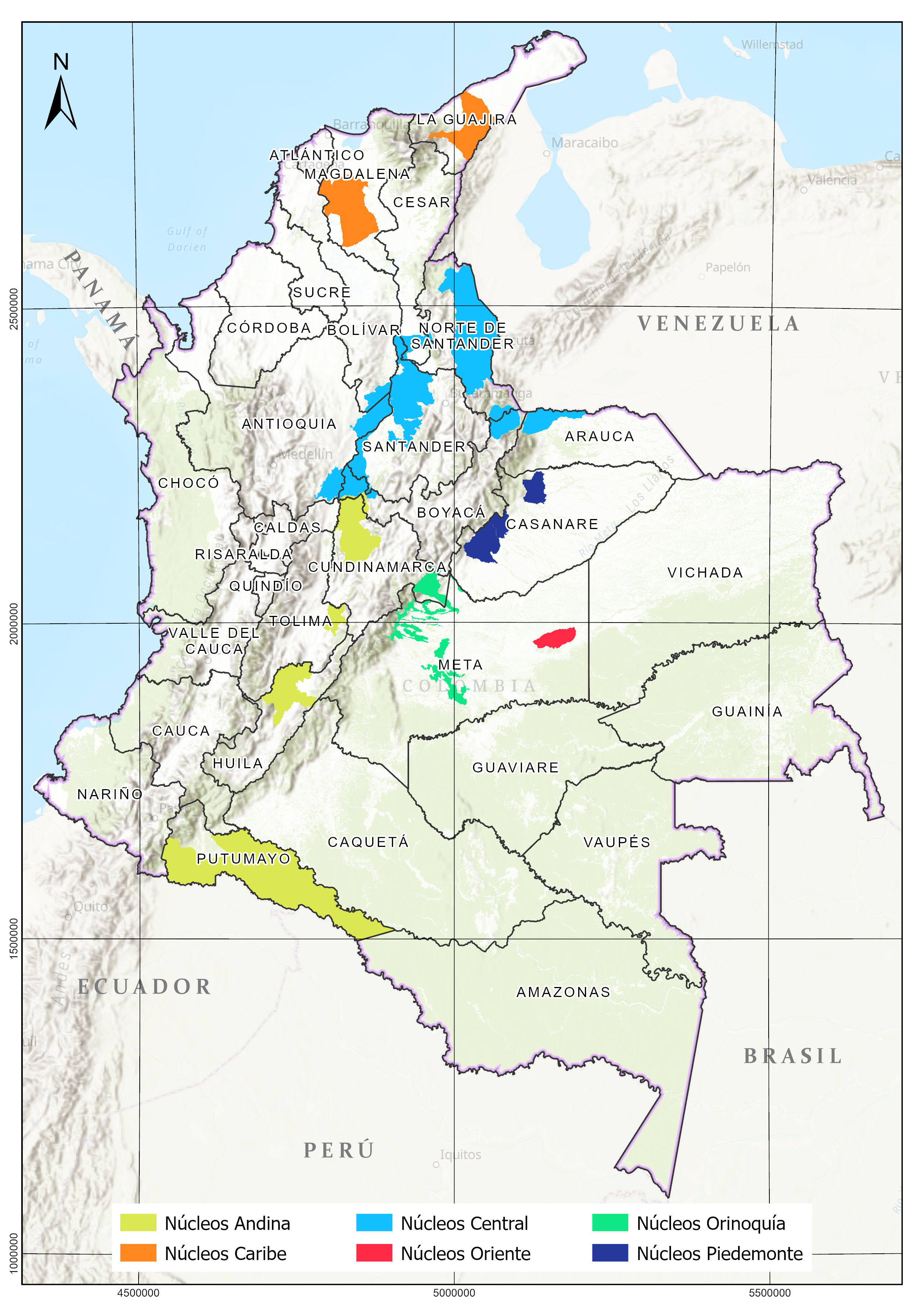
At this link you can find testimonials of participants in voluntary conservation agreements, within compliance of biodiversity offsets and mandatory 1% investments. Voluntary conservation agreements in Piedemonte-Casanare Region
Activities developed within voluntary conservation agreements
Voluntary conservation agreements are one of the most widely used modes for compliance of biodiversity offsetting and mandatory 1% investment within the company. These agreements formalize through a civil contract between Ecopetrol S.A. and land-owners, and include a series of conservation actions and in-kind payments for sustainable biodiversity use. This scheme enables the protection of areas with high-ecological value, while offering benefits to participants that result in improved quality of life and land productivity. Conservation and sustainable use actions implemented within voluntary conservation agreements are described below.

Some of the activities developed within voluntary conservation agreements incluide:
Biodiversity baseline and monitoring
Characterizations of the initial ecosystem state before the development of preservation and/or rehabilitation actions and periodic monitoring to identify biodiversity gains in areas under voluntary conservation agreements. These assessments encompass both, biotic and abiotic components of the areas of interest before, during and at the closure of the agreement. Examples of species found in areas under voluntary conservation agreements, shown below.


Fauna in agreement conservation areas. left: Mono capuchino (Cebus capucinus) Source: Ecopetrol S.A Central environmental Coordination. Rignt: Jacamará bardiblanco (Galbula bardiblanco) Source: Ecopetrol S.A Piedemonte environmental Coordination.
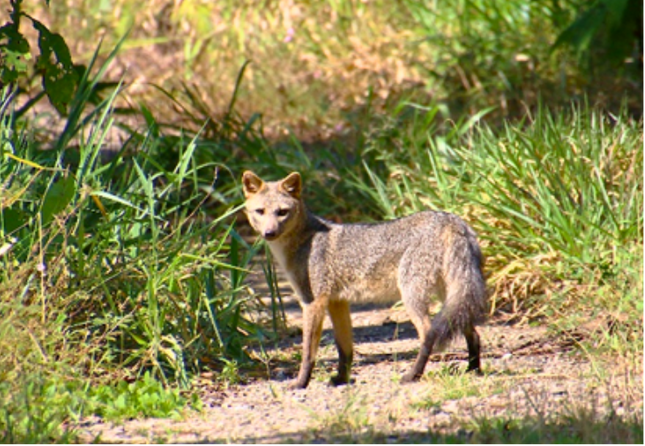


Fauna in agreement conservation areas. Left: Zorro cangrejero (Cerdocyon thous) Source: Ecopetrol S.A Piedemonte environmental Coordination. Right: Venado (Odocoileus cariacou) Source: Ecopetrol S.A Oriente environmental Coordination
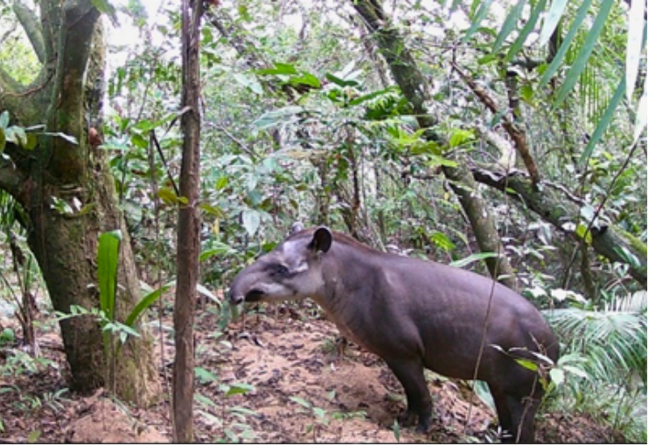


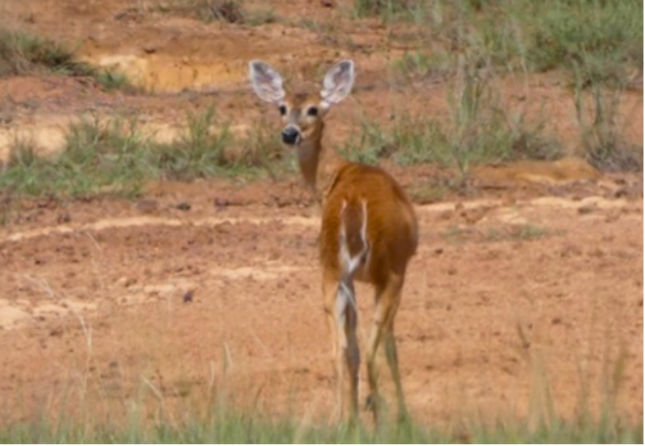
Fauna in agreement conservation areas. Left: Juvenil de rana platanera (Boana pugnax) Source: Ecopetrol S.A. Central environmental Coordination. Right: Danta (Tapirus terrestris) Source: Ecopetrol S.A. Oriente environmental Coordination.
Isolation of areas designated for conservation/rehabilitation along with establishment of in-kind incentives (forest-grazing systmes, agroforestry, dendroenergetic orchads)
This entails the installation of isolation fences using materials like concrete, wood, or plastic posts, along with barbed wire or other fencing materials, around the designated areas for rehabilitation or preservation. Additionally, in-kind incentives are provided within the property to support these efforts.
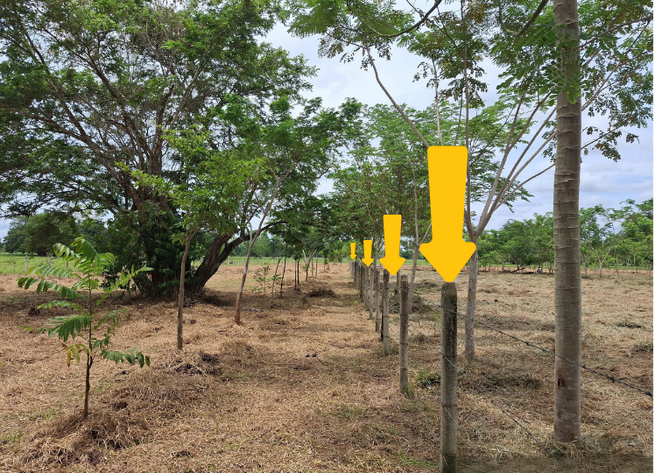
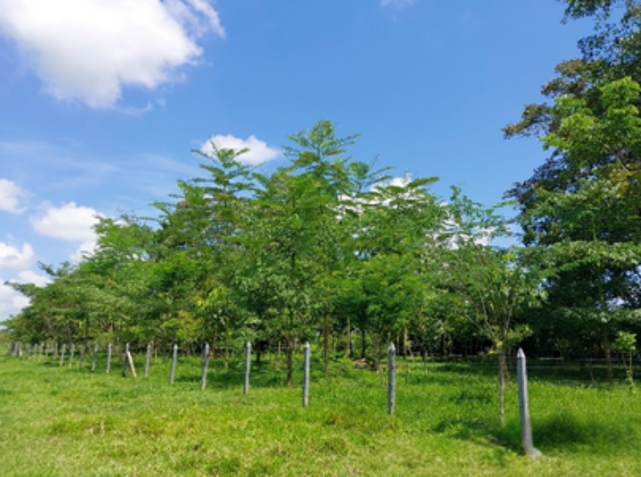


isolation of strategics areas targeted for sustainable forest-grazing use. Source: Ecopetrol S.A Central environmental Coordination.
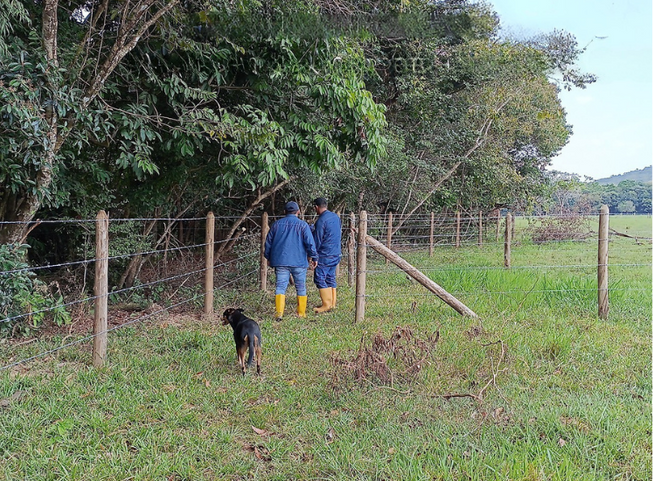

Isolation of strategics areas: Left. Targeted for conservation. Source: Ecopetrol S.A. Piedemonte environmental Coordination. Right targeted for conservation. Source: Ecopetrol S.A Orinoquia environmental Coordination.
Preparation and adaptation of plant material.
To enhance rehabilitation success on the farms, we ensure that the plant material meets the necessary survival conditions, which vary depending on the species, planting density, terrain conditions, among others.
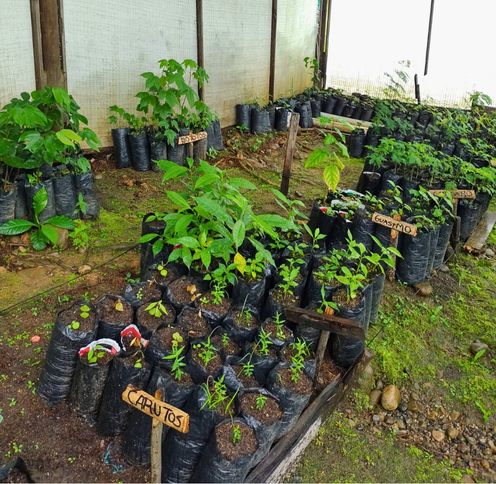
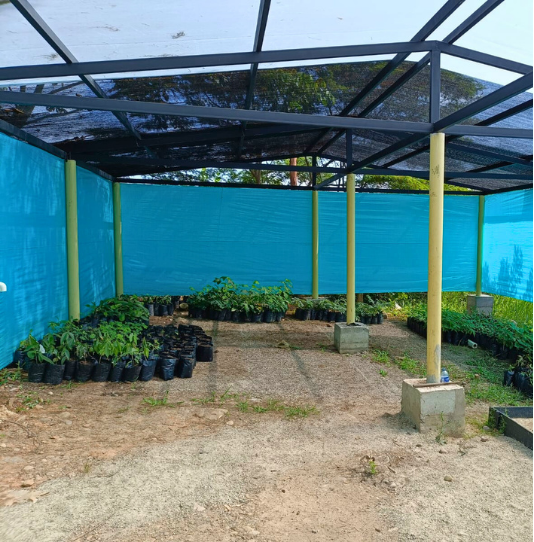


Nursery to produce plant material for conservation actions. Source. Ecopetrol S.A. Piedemonte environmental Coordination.
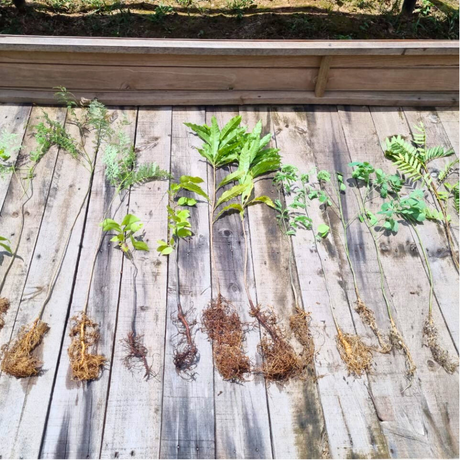


Measurement and verification of physical and phytosanitary conditions of plant material. Source: Ecopetrol S.A. Oriente environmental Coordination.
Establishment of in-kind incentives and rehabilitation areas
It consists of the implementations of sustainable use schemes such as agroforestry and/or forest-grazing systems. As agreed, upon with each signatory of the voluntary conservation agreement. These systems are incentives that generate added value for conservation actions, as they represent improved productive opportunities and improved quality of life for the signatories.


Agroforestry systems with plantain in the departments of Huila and Putumayo. Source: Ecopetrol S.A Andina environmental Coordination.


Right agroforestry system. Left silvopastoral system of the municipality of Acacías. Source: Ecopetrol S.A Environmental Coordination Oriente with partner B.Q.S S.A.S.

Delivery of eco-efficient stoves. Source: Ecopetrol S.A Central and Andina environmental Coordination.
Capacity building
In voluntary conservation agreements, Ecopetrol S.A. actively promotes the development of local communities by providing technical assistance and socio-environmental training. These initiatives cover a range of topics including good practices in agroforestry tailored to crops like cocoa, banana, and citrus fruits, as well as practices concerning forest-grazing systems, animal health, and livestock sector regulations. These training sessions are led by experienced professionals working in collaboration with both local and national institutions.
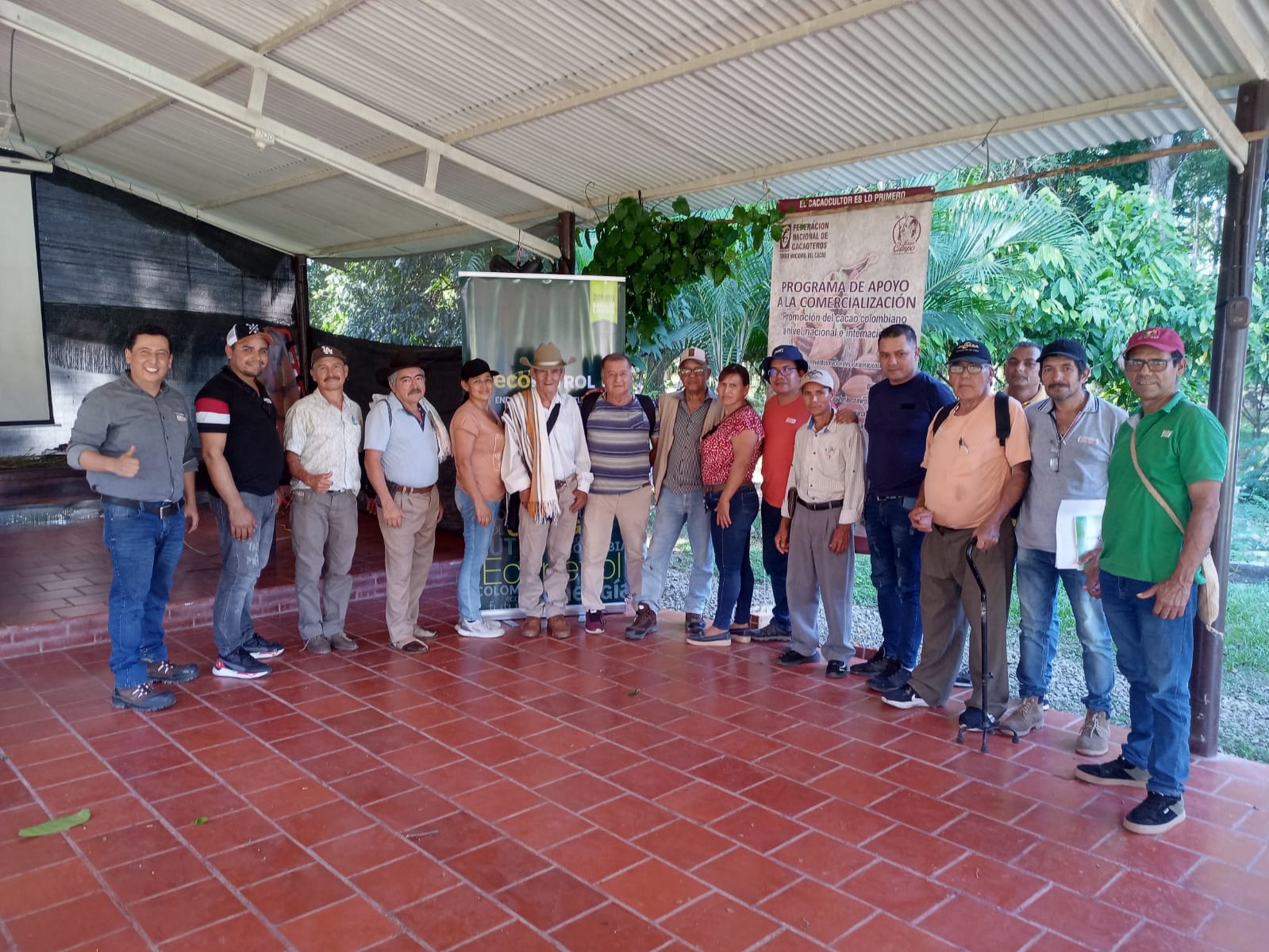


Training out at the Gibraltar gas field in conjunction with FEDECACAO. Source: Ecopetrol S.A. Central environmental Coordination.
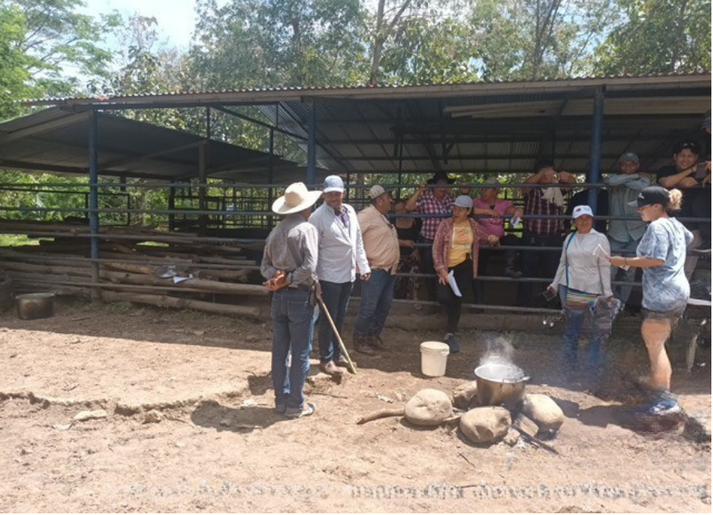


Theoretical – practical workshop held in the municipality of Aguazul in conjunction with FEDEGAN. Source: Ecopetrol S.A Piedemonte environmental Coordination.
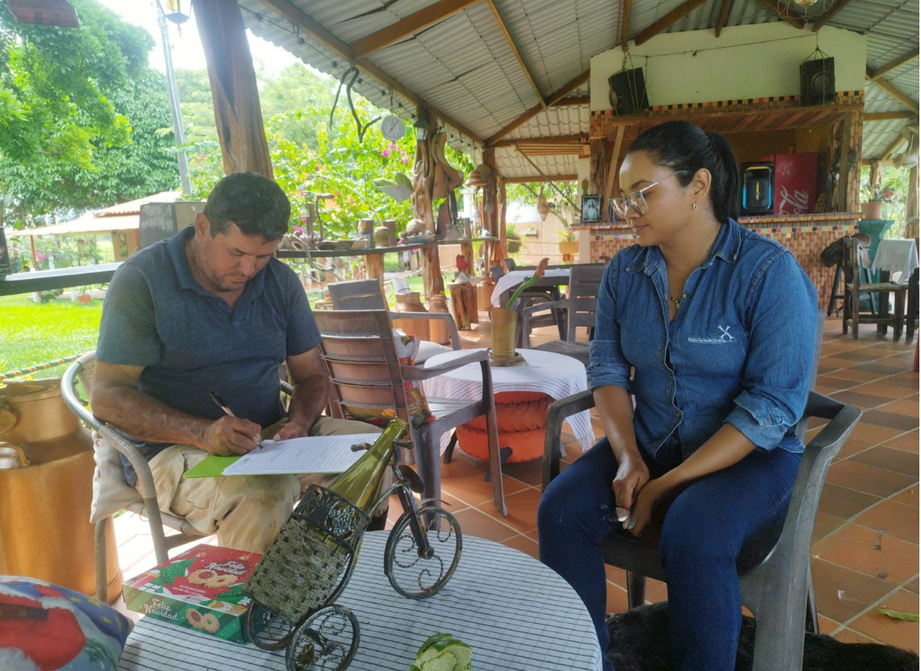
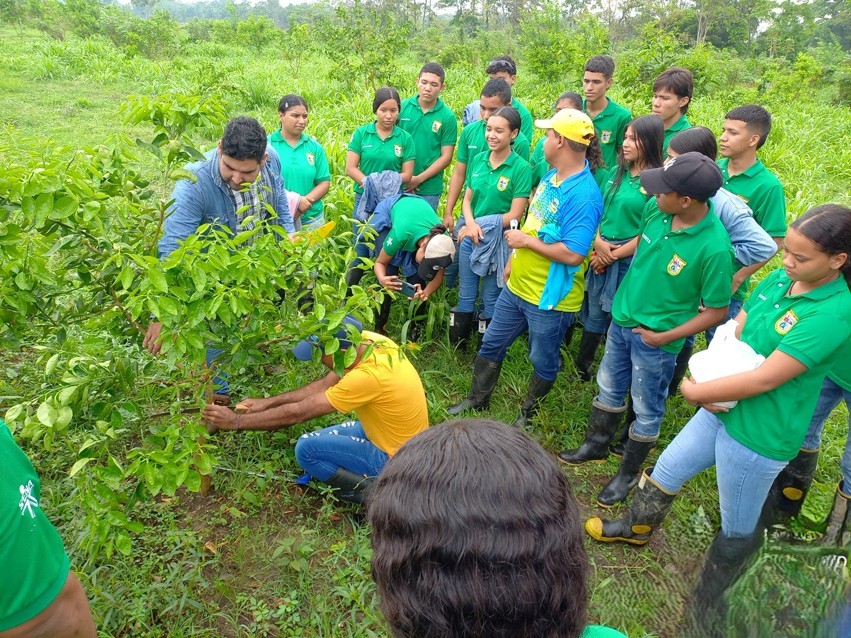


Left: technical assistance in agroforestry systems. Source: Ecopetrol S.A Central environmental Coordination. Right: VCA satisfaction and compliance survey. Source: Ecopetrol S.A Environmental Coordination Oriente with partner B.Q.S S.A.S
Restoration actions in biodiverrsity offsets and mandatory investment of no less than 1%
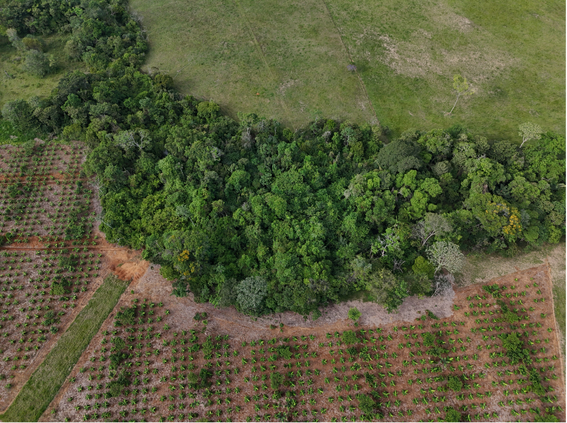
Ecopetrol S.A. implements restoration actions from three approaches: ecological restoration, which seeks to reestablish the structure and function of degraded ecosystems so that they are self-sustaining and ensure species conservation; rehabilitation, to restore productivity and ecosystem services; and recovery, to restore the usefulness of ecosystem services to the territory, integrating it in into its environment (Plan Nacional de Restauración, 2015). Within the framework of these actions, Ecopetrol implements actions that promote ecological processes such as seed dispersal through substrate adjustments and foraging through the installation of perches. Many of these initiatives are conducted in a participatory manner with local communities, involving them throughout the entire process.
Ecologic rehabilitation in the municipality of Rio Negro, Santander. Fuente: Central environmental Coordination.
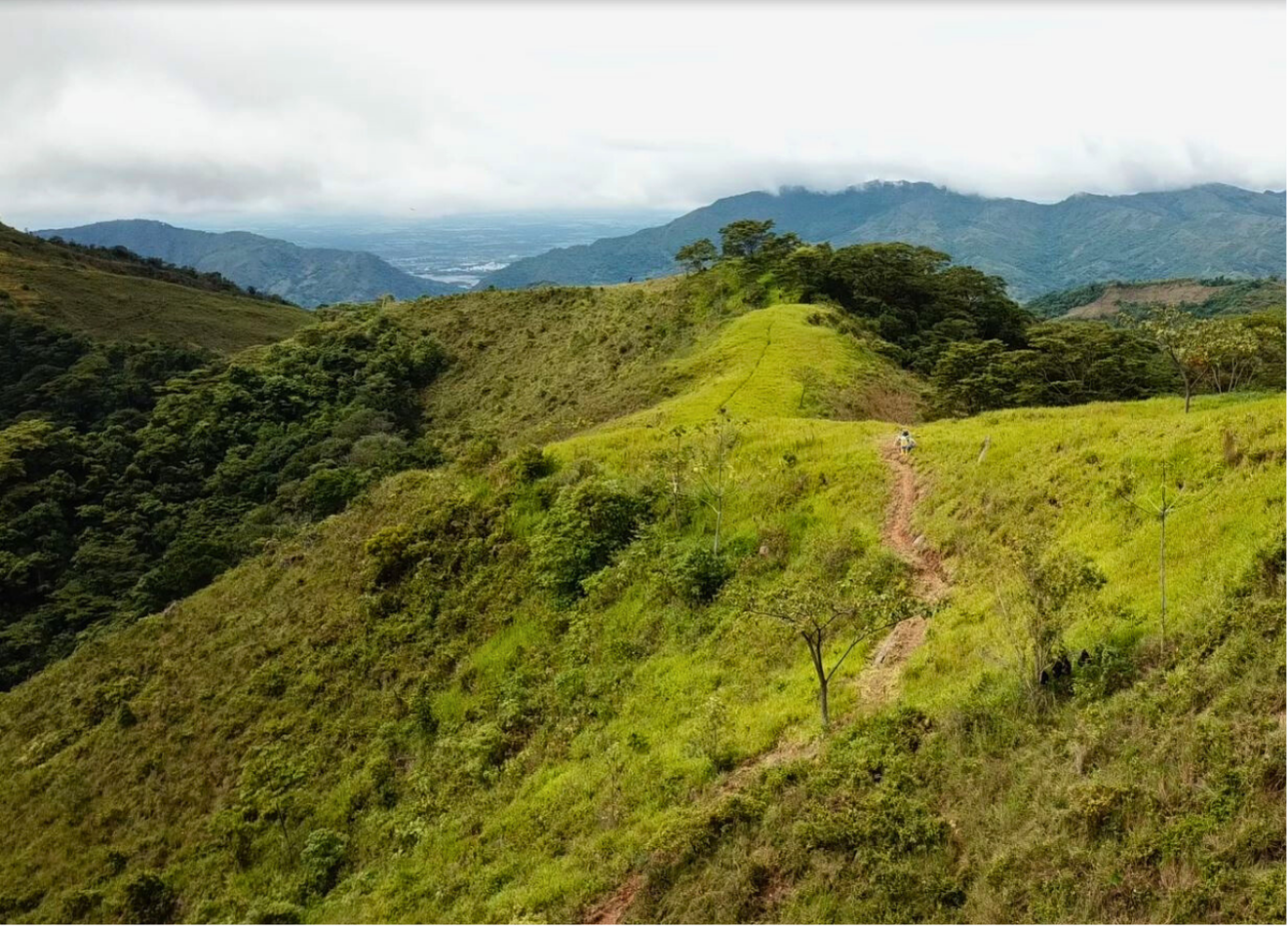
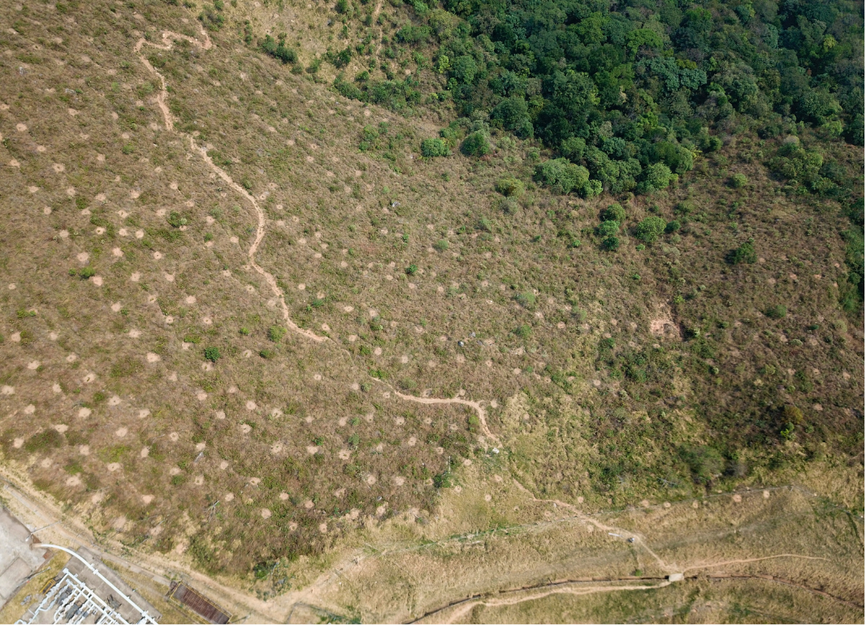




“Re-viva La Primavera” Project, an ecological restoration Project in the municipality of Yopal, Casanare. Source: Piedemonte environmental Coordination.
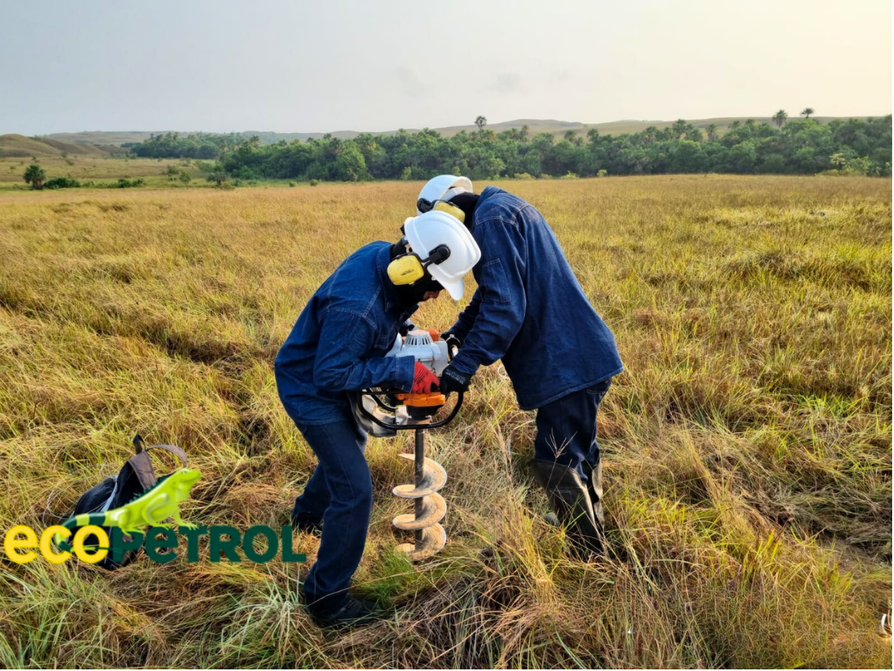
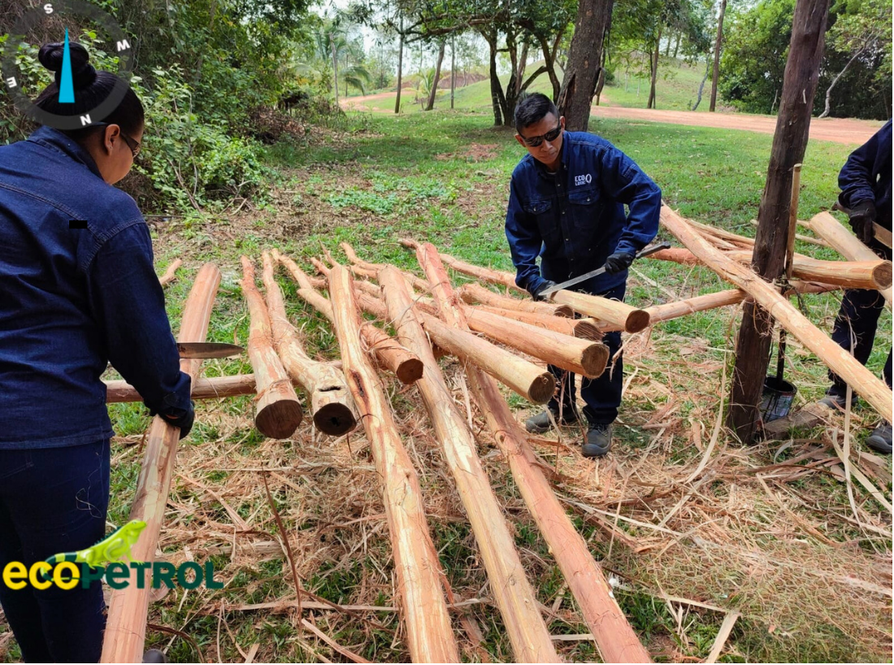
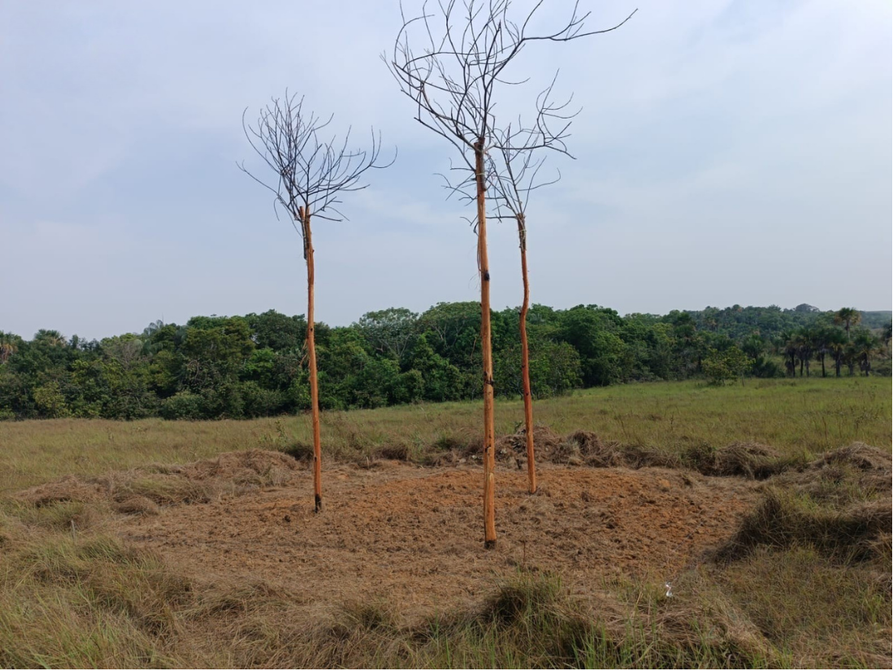
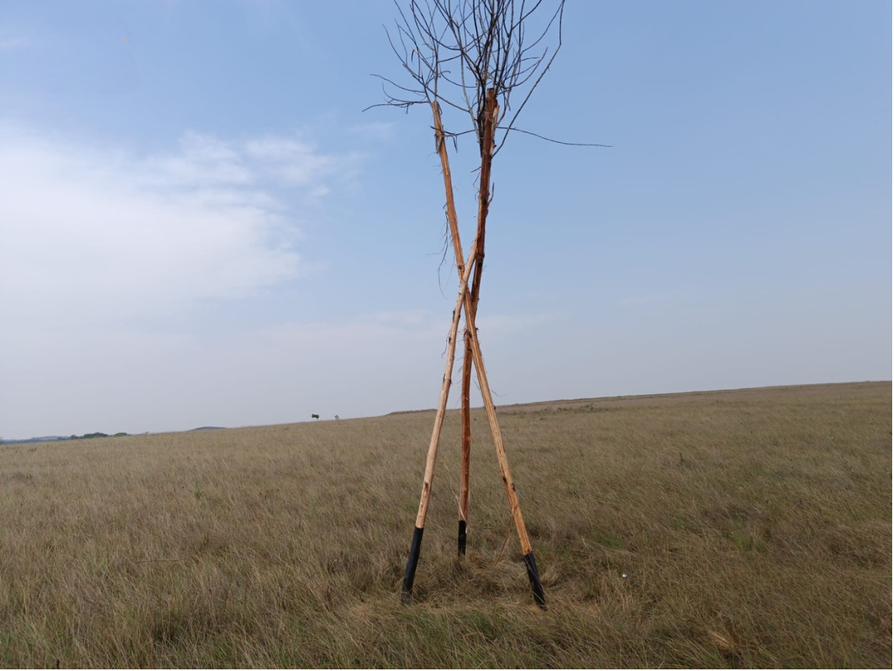




Implementation of artificial perches as bird attractants. Wood drilling, debarking, island, and individual perches. Source: Ecopetrol. S.A Oriental environmental Coordination.
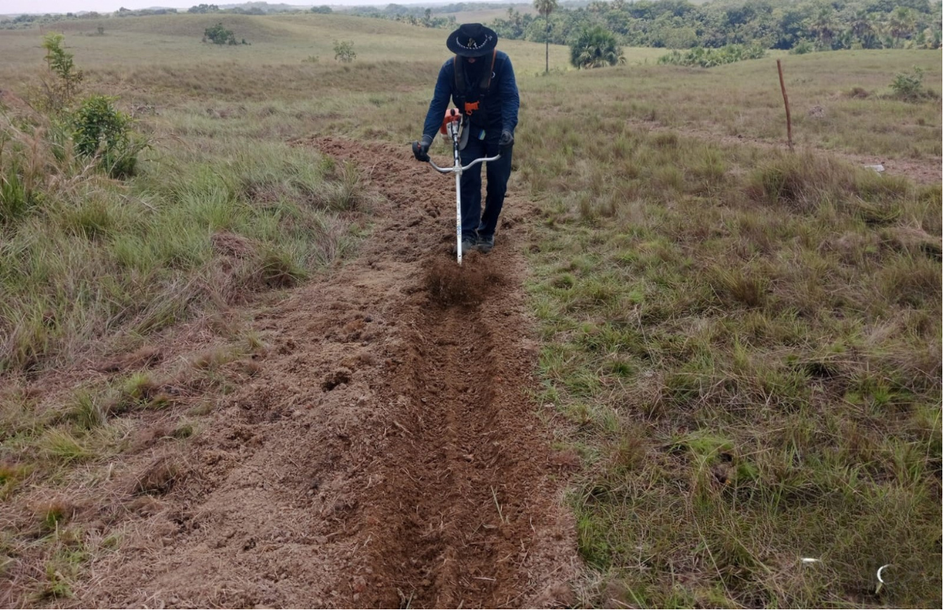
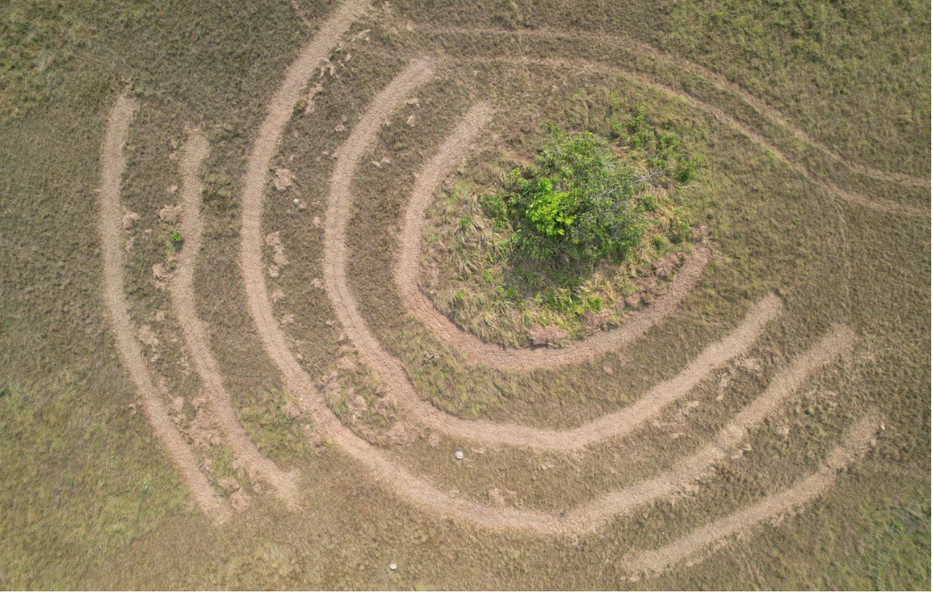


Actions to encourage seed dispersal. Plowing and trenches for seed capture. Source: Ecopetrol S.A Oriental environmental Coordination

Goals in biodiversity offsets and mandatory investment of no less than 1% by 2030
 |
Carry out conservation actions that encompass preservation, conservation, and sustainable use on approximately 15.000 hectares nationwide. |
 |
Upgrade 15 hydrological / meteorological stations in the hydrographic sub-zones of the Cusiana and Cravo Sur rivers in the department of Casanare in partnership with IDEAM. |
 |
Implement ecological restoration actions on more than 3.000 hectares |
Compliance results in biodiversity offsets and 1% investment 2024
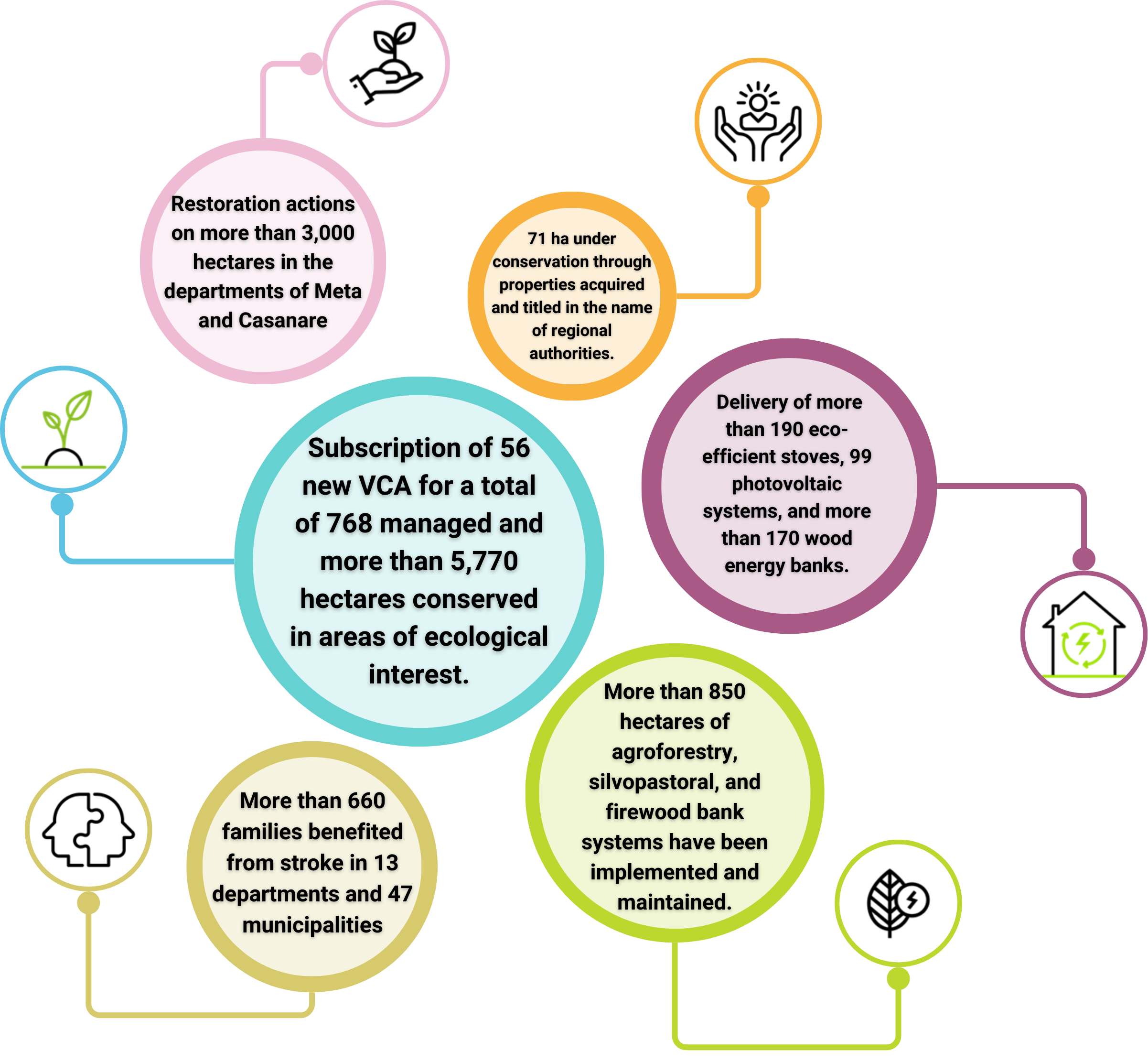
In compliance with our obligations, Ecopetrol has implemented 103 forced investment plans of no less than 1% and 161 biodiversity offset plans that contribute to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity on more than 9000 hectares. These plans have been approved and endorsed by the Environmental Authority and focus on programs that not only comply with legal obligations but also contribute to community development.
. . .