PautaInternas
PautaInternas
 buscador
buscador
 Risk Management at Ecopetrol
Risk Management at Ecopetrol
Risk Management at Ecopetrol
Jan 27, 2026
Ecopetrol’s Corporate Governance Code identifies risk management as one of the best practices in transparency, governance, and control, as follows
“ECOPETROL operates in a highly dynamic and uncertain industry. Therefore, it must manage risks and internal control comprehensively to seize opportunities and mitigate adverse effects on the Company’s interests. Integrated risk management at Ecopetrol seeks to establish general guidelines for risk administration and to foster a culture that enables informed decision-making, considering potential events that may positively or negatively impact the Company’s objectives.”
To learn more, please consult:
https://www.ecopetrol.com.co/.../Anexo+2+C%C3%B3digo+de+Buen+Gobierno+de+Ecopetrol.pdf
The Integrated Risk Management System (IRS) is based on the ISO 31000:2009 standard. Through this system, a set of principles, a reference framework, and a process (Single Risk Management Cycle) are established, enabling the organization to manage the effects of uncertainty on the achievement of objectives. The aim is to maximize opportunities and support the development of strategies, the achievement of objectives, and informed decision-making, as shown below:
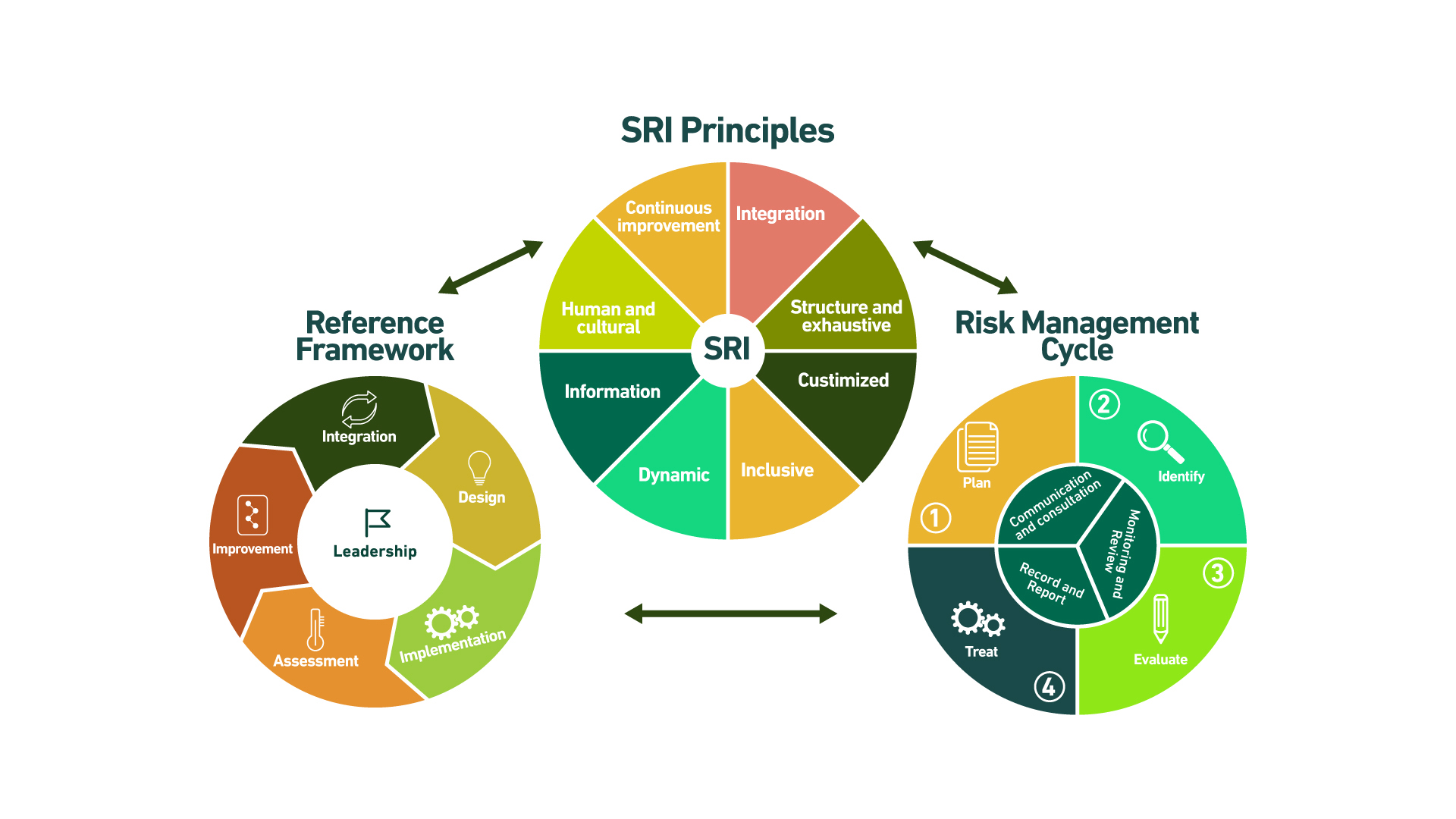
This system is led by the Corporate Compliance Office through the Risk Management Office and is overseen by the Board of Directors through its Audit and Risk Committee, in accordance with the roles and responsibilities detailed below.
According to Ecopetrol S.A.’s Corporate Governance Code, “ECOPETROL has established an organizational structure that supports risk management and the Internal Control System, assigning specific responsibilities to the Board of Directors, the Audit and Risk Committee, the President, and the Risk Management and Internal Control areas under the Compliance Vice Presidency.”
Indeed, Ecopetrol S.A. defines oversight, execution, and reporting responsibilities within the framework of the Integrated Risk Management System, as follows:
Board of Directors:
- Approve the Code of Ethics and Conduct and the guidelines of the “Compliance Program System,” which includes the Integrated Risk Management System, the Internal Control System, and the Compliance Management System.
- Ensure the effectiveness of the internal control and risk management systems.
Audit and Risk Committee of the Board of Directors:
- Verify the establishment of the Risk Management System, which must include the identification, assessment, treatment, and monitoring of the Company’s risks, their materialization, and the corresponding analysis of the impacts of potential risk events.
- Analyze and recommend to the Board of Directors the approval of Ecopetrol S.A.’s Corporate Risk Map, in alignment with strategic objectives, and monitor the status of its management.
- Recommend to the Board of Directors the approval of guidelines for the retention, transfer, and mitigation of financial risks, including insurance for the Ecopetrol S.A. Group.
- Approve the General Audit Plan (GAP) based on the corporate risk map, ensuring the adoption of standards and the application of internationally accepted auditing practices, and monitor its implementation.
Chief Executive Officer:
- Establish, maintain, and evaluate the effectiveness of the Company’s Internal Control and Integrated Risk Management Systems. Present, together with the Compliance Officer, the guidelines of the “Compliance Program System” and reports on its effectiveness for approval by the Board of Directors.
Vice presidencies, Offices and Management Areas:
- Provide the necessary resources for the implementation of methodologies for managing the types of risks under their responsibility.
- Review and monitor the measures implemented for risk management.
- Report the required information for monitoring the Integrated Risk Management System.
Corporate Compliance Office:
- Lead the Integrated Risk Management System (IRS) as an independent function (second line of defense), through the Risk Management Office (RMO), ensuring the design, implementation, administration, sustainability, and continuous improvement of the IRS.
- Additionally, with respect to the Group companies, exercise governance, provide guidance, issue standards, define practices, and monitor risk management activities to unify guidelines and promote synergies, with the objective of enabling timely and well-informed decision-making.
Risk Management Office:
- Design, implement, manage, and maintain the Integrated Risk Management System for the Ecopetrol Group, as well as define the system’s guidelines and the risk management cycles at the strategic and tactical levels.
All Ecopetrol S.A. employees:
- They are responsible for executing daily tasks with commitment, rigor, and attention to detail. They must also identify, assess, address, control, and communicate the risks to which we are exposed, in alignment with the principles, framework, and processes of the Integrated Risk Management System (IRS), and in adherence to the Code of Ethics and Conduct.
Internal Audit Office:
- Responsible for carrying out their daily tasks with commitment, rigor, and attention to detail. They are also expected to identify, assess, treat, control, and communicate the risks to which the organization is exposed, in compliance with the principles, framework, and process of the Integrated Risk Management System (IRS), and in observance of the Code of Ethics and Conduct.
Risk appetite refers to the level of risk the company is willing to assume in the pursuit of its objectives, and it guides risk-based decision-making.
Ecopetrol’s expression of risk appetite is framed within the company’s strategy and its Corporate Governance Code.
Risk tolerance refers to the acceptable outcomes or variations in relation to the achievement of objectives. Some zero-tolerance risks at Ecopetrol include:
- Fatalities occurring during the execution of company operations.
- Practices that breach the Ecopetrol Group’s Code of Ethics and Business Conduct.
- Actions that breach regulations related to environmental protection, personal safety, community well-being, and other stakeholder interests.
In addition, there are certain parameters that complement the company’s risk appetite:
- Strategic risk parameters: For example, new products to be introduced, products to be avoided, and capital expenditure investment focus.
- Financial risk parameters: For example, the maximum acceptable level of loss or performance variation, including variability in earnings per share, free cash flow growth/margin, earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT)/margin, return on assets, and EBITDA return percentage.
- Operational risk parameters: For example, expected sustainability response, existing/projected environmental requirements, safety targets, quality objectives, and customer criteria and concentrations.
Within the framework of the Integrated Risk Management System, risks are classified as strategic, tactical, or operational, depending on the level at which they are managed.
At each of these levels, risks are managed in accordance with the specific regulations and standards adopted by the company.
Examples of risks managed at the operational level include:
- Risks associated with new business opportunities, including the management of investment and divestment initiatives.
- Commercial risks related to domestic and international markets.
- Project-related risks.
- Exploration activity risks.
- Financial risks – including credit, liquidity, and market risks.
- Cybersecurity and information leakage risks.
- HSE risks – encompassing occupational health, environmental, industrial safety, and process safety risks.
- Compliance risks – including fraud, money laundering, terrorist financing, and the financing of the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
The risk management process is grounded in the systematic application of Ecopetrol’s Unified Risk Management Cycle, which applies to all types of risks across the strategic, tactical, and operational levels.
This cycle must be executed for all risk categories, consistently oriented toward the achievement of objectives, taking into account both internal and external contexts, while also incorporating the specific methodological frameworks relevant to each risk type.
RISK MANAGEMENT CYCLE
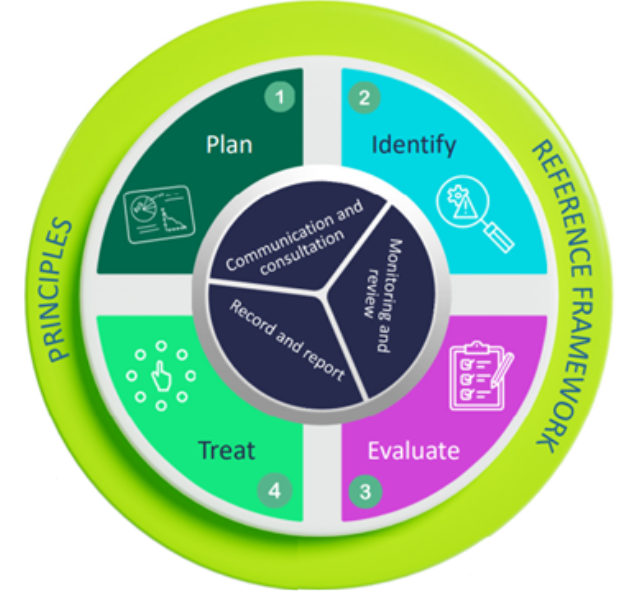
The Unified Risk Management Cycle is executed based on the following stages, which guide the systematic activities to be carried out.
- Plan: Define the scope of activities and analyze both internal and external contexts.
- Identify: Identify risks based on stakeholder perspectives and information analysis.
- Assess: Analyze causes and consequences. Evaluate risks based on likelihood and impact.
- Treat: Select and implement appropriate risk response option.
- Communicate, Monitor, and Record: Ensure continuous information exchange, feedback, and periodic review of risk exposure. This includes identifying alerts, verifying the implementation of mitigation measures, and ensuring actions are taken in response to materialized risks, with the goal of keeping risks within defined tolerance and acceptance levels.
Ecopetrol applies a risk assessment matrix that includes descriptive scales for the likelihood of occurrence and the impact across various dimensions such as people, environment, economic resources, reputation, and customers.
Based on the combination of likelihood and impact, risk levels are categorized as Very High, High, Medium, Low, and Very Low.
The matrix defines:
- Non-tolerance zone, where the risk must be actively managed.
- Tolerance zone with controls, where the risk is managed through mitigation measures.
- Acceptance zone, where the risk is assumed by the company.
Risk assessment considers the magnitude of consequences and the likelihood of occurrence, providing essential input for prioritizing risks and making informed decisions regarding their treatment.
This risk assessment includes the calculation of both inherent and residual risk levels, based on the defined probability and impact scales, as well as the tolerance and acceptance thresholds established in the Risk Assessment Matrix.
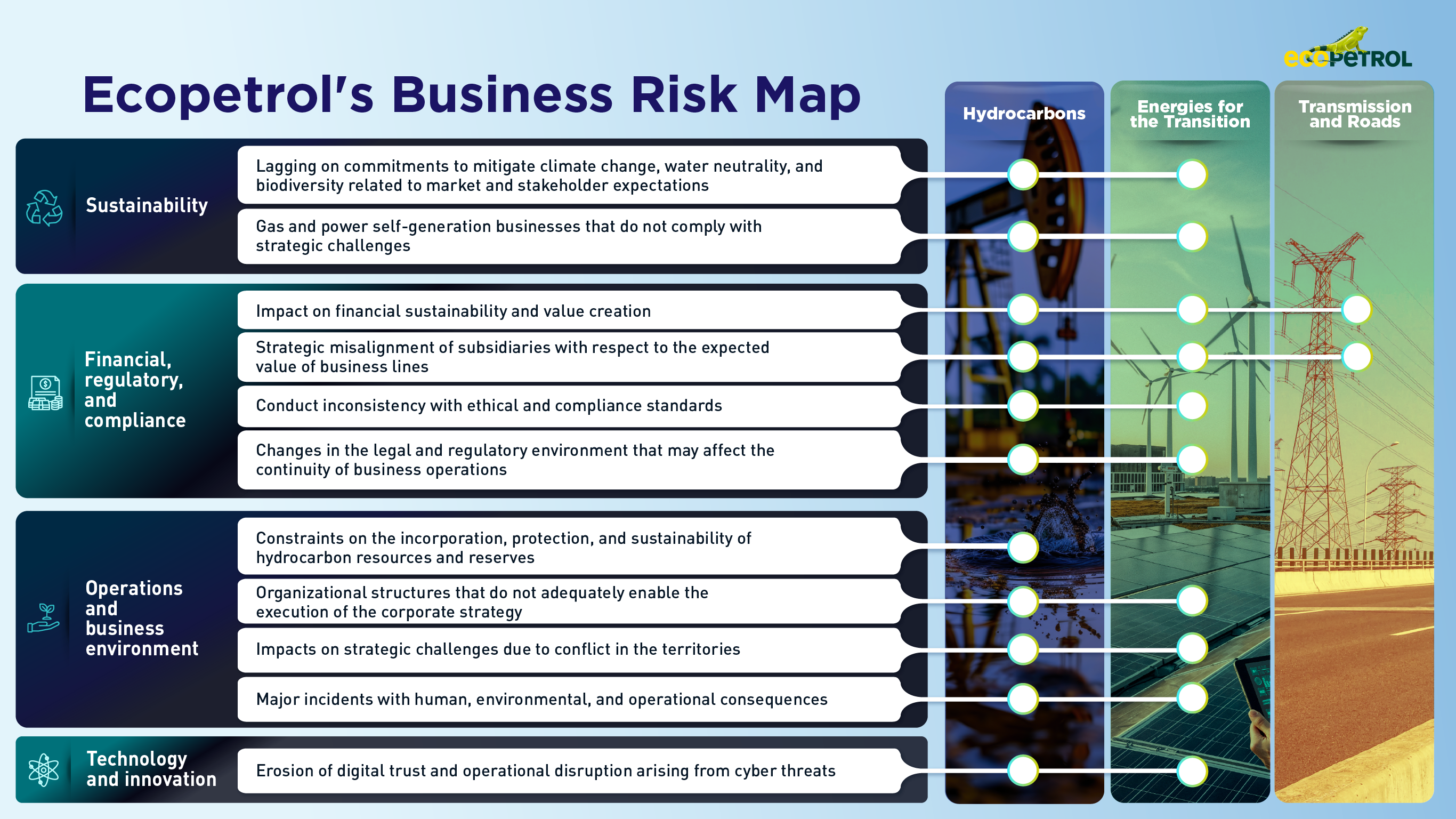
The Corporate Risk Map reflects the events that, in the judgment of Ecopetrol S.A.’s Board of Directors and Senior Management, could potentially divert the company from achieving its strategic objectives and/or its balanced scorecard goals.
Ecopetrol periodically reviews and updates the risk map.
Below is the current Corporate Risk Map of Ecopetrol S.A.:
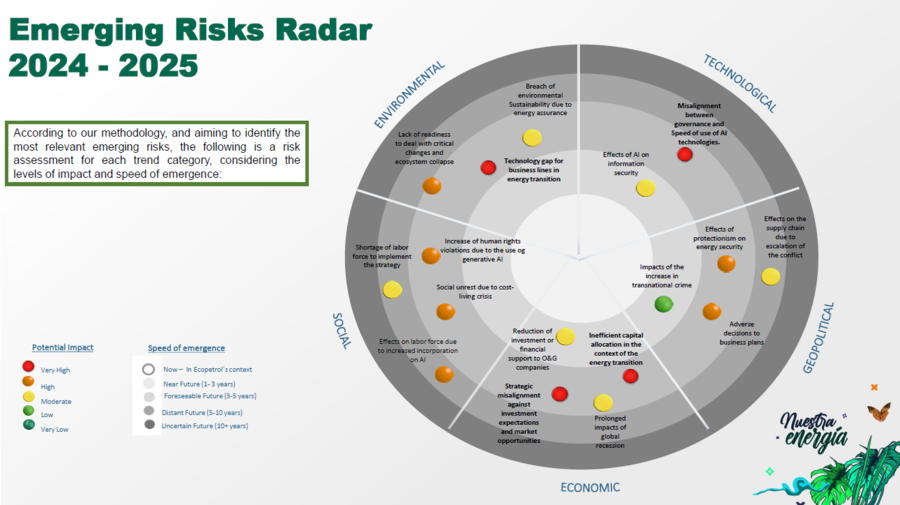
Ecopetrol defines emerging risks as those that could have a long-term impact on the company (3–5 years or more), or in some cases, may have already begun to affect the organization.
Based on the analysis conducted, emerging trends for Ecopetrol were identified and classified into the following categories: Social, Environmental, Economic, Technological, and Geopolitical.
From these trends, emerging risks were identified and assessed, as shown below:
Ecopetrol’s Emerging Risk Radar